Information for Group Managers
A group manager is a person authorized to manage group course or private cluster course.
By default, the group manager is set to the service course applicant. The applicant of the service course can add/change the group manager. Please apply for add/change via User Portal.
A group manager can use the commands for managing the group. The dedicated commands of group manager allow group managers to manage queues and disks allocated to their groups and group members.
Group members can be managed by logging into the User Portal.
- After logging in to the User Portal, click “Service Application” on the top menu
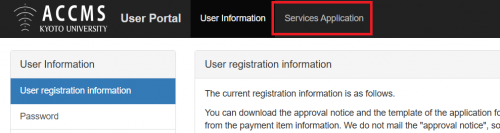
- Click “Group members” on the left menu.
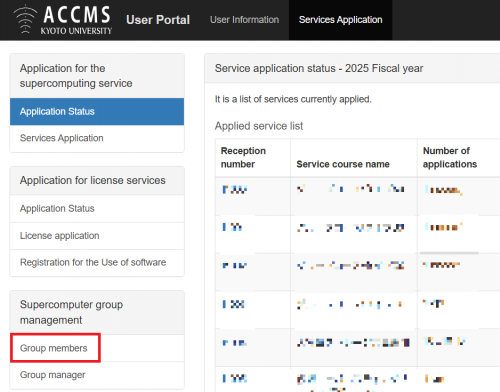
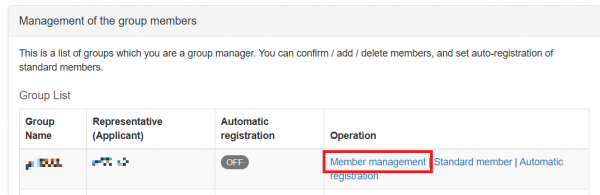
- You can check and add/delete members from “Member management”.
You can make backup settings of the LARGE disk space by using the group_backup command. LARGE disk space consists of the /LARGE0/groupname directory and the /LARGE1/groupname directory, and you can set one of the following status.
| Status | /LARGE0/groupname | /LARGE1/groupname |
|---|---|---|
| Backup | Safe(Make backup) | Backup (Backup location) |
| Not Backup | Unsafe(Not make backup) | Unsafe(Not make backup) |
Of these, disks whose settings are Safe or Unsafe can be used.
Checking the backup settings
The target group can be specified with the -g option. If omitted, the current group when the command is executed is targeted.
$ group_backup -g gr19999 -l
Num Filesystem Status Filesystem Status
1) /LARGE0/gr19999 ... Safe /LARGE1/gr19999 ... Backup <- バックアップ使用状態Setting the status to “Not Backup”
$ group_backup -g gr19999 --unsafe 1
/LARGE0/gr19999: Safe => UnSafe
/LARGE1/gr19999: Backup => UnSafeChecking the backup settings(after changes)
$ group_backup -g gr19999 -l
Num Filesystem Status Filesystem Status
1) /LARGE0/gr19999 ... UnSafe /LARGE1/gr19999 ... UnSafe <- バックアップ未使用状態Return to the status to Backup
$ group_backup -g gr19999 --safe 1
/LARGE0/gr19999: Unsafe => Safe
/LARGE1/gr19999: Unsafe => BackupThe group_trash command allows users to delete files(move to trash) in the LARGE disk space. It can delete the data files of users who are no longer enrolled due to graduation, etc. If you accidentally delete a file, you can recover it from the trash, but please note that the trash is emptied every Monday.
Deleting files by the group_trash command
Specify the target group with the -g option. If omitted, the group manager authority are determined by the current group when the command is executed.
$ group_trash -g gr19999 /LARGE0/gr19999/file1
file1 to Trash (/LARGE0/gr19999/.DpcTrash/b59999/2009-04-10_1010)There are two types of units of management of Slurm queue privileges: users and groups. Users are empty by default, Groups are initially registered with the group corresponding to the queue name as the default setting.
If you wish to use a queue with multiple groups, or if you wish to grant queue access to a single user who does not belong to a group, please contact us using the Inquiry Form.
You can select the job scheduling policy from the following three types. If you are using an individual queue (grXXXXXx), you can change your preferred scheduling policy by contacting us from the applicant at Inquiry Form. (We cannot accept requests for shared queues such as entry course or personal course.)
| Settings | Operation |
|---|---|
| pass | If there are sufficient computing resources to execute a job, it will overtake jobs waiting to be executed that are in line before it. You can use computing resources efficiently, but large jobs may not be executed indefinitely.【Default Value】 |
| wait | It will not overtake jobs even if there is a enough computing resources. |
| backfill | Based on the calculations of the execution time limit (-t) of each job, it will overtake jobs only if it does not affect the execution start time of other jobs. For example, you can use resources effectively by executing small jobs that can complete execution before a large job is started. |
You can confirm the job execution status of queues registered as a group manager and cancel the jobs with the spadmin command.
-
Confirmation of job execution status
$ spadmin list -p gr19999b ## Please change the "gr19999b" part to the queue name you wish to confirm. JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON) 4781 gr19999b run_cpu2 b59999 R 1:26:09 1 nb0001 -
Cancellation of the job
$ spadmin cancel 123 scancel: Terminating job 123
If anyone other than the group manager execute the spadmin command, the following error message will be displayed.
$ spadmin list -p gr19999g
Authorization Failure